Introduction.
In 2020, according to the international diabetes Federation (IDF) , 463 million people have diabetes in the world and 88 million people in the south-east Asia region suffer from diabetes. Of these 88 million people, 77 million belong to India.
Although the cause of diabetes is due to is multiple metabolic disorders and variable risk factors, the main reason that makes an individual a diabetic is either due to lack of insulin or the body developing resistance to insulin. The most potent treatment for diabetes is insulin therapy itself.
Today let us learn what insulin is and why it is called the king molecule.
What is insulin?
Insulin is naturally produced by the Pancreas. It is an organ located in the abdomen. It has two main functions ; exocrine (98%) and endocrine (2%).
The endocrine portion of the pancreas is also known as the islet of Langerhans. It regulates the blood sugar levels in the body. This part of pancreas has four main types of cells that produce their own respective hormones. They are as follows:-
- α-cells:- Glucagon
- β-cells:- Insulin.
- δ-cells:- Somatostatin.
- F-Cells:- Pancreatic polypeptide.
The beta cells are present in maximum number and produce insulin that plays an important role in regulating glucose metabolism.
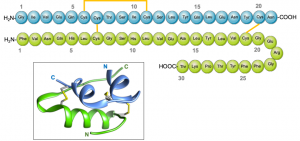
Structure of insulin.
Insulin is a large protein made up of 51 amino acids in 2 chains. These 2 chains contain 21 and 30 amino acids respectively and are linked together by sulphur atoms(disulphide bonds)
That being said, we have understood what insulin is, basically.
Now let us get into the facts about why this polypeptide is called as the king molecule.
Insulin is considered as the major anabolic hormone in the body due to its various effects on metabolism.
Effects on Carbohydrate Metabolism.
INsulin has 3 main functions in carbohydrate metabolism.
- Firstly, The glucose uptake in adipose tissue and muscles are purely dependent on insulin.
- Secondly, Insulin increases glycogen synthesis and decreases glycogenolysis.
- Thirdly, It decreases gluconeogenesis in the liver.
Effect on Lipid Metabolism.
Insulin keeps lipolysis under check with the help of hormone sensitive lipase.
Lipolysis is nothing but breakdown of fat. As a result,there is increased level of FFA (free fatty acids) in the blood. When these FFA enters the liver it is broken down into glucose, triglycerides, VLDL. This can lead to another condition known as Ketosis.
Hence, keeping Lipolysis under check is a vital function of Insulin.
Effects on Protein Metabolism.
Insulin helps in :
- Increased uptake of amino acids.
- increase in protein synthesis.
Effect on potassium transport.
Insulin activates Sodium-potassium ATPase channel which is important in maintaining sodium potassium homeostasis.
Due to these various activities carried out by insulin, it is referred to as the King molecule.
Normal levels of Insulin.
| Insulin level | |
| Fasting | <25mIU/L |
| 30min after glucose administration | 30-230 mIU/L |
| 1 hour after glucose administration | 18-276 mIU/L |
| 2 hours after glucose administration | 16 – 166 mIU/L |
| >3 hours after glucose administration | <25 mIU/L |
What happens when insulin level is high?
The condition where the insulin level is high is called as hyper-insulinemia. It has been directly linked to obesity, heart disease and cancers.
High insulin levels in the blood can also cause your cells to become resistant to the hormones effects. When your body becomes resistant to insulin, The pancreas produces even more insulin creating a vicious cycle.
What happens when insulin level is low?
Low insulin level manifests as hyperglycaemia. Effective salute will not cross the cell membranes hence water is drawn out from the cells. This can lead to Glycosuria and osmotic diuresis (polyuria, polydypsia, polyphagia).
Decrease in the insulin level can also lead to negative nitrogen balance. This in turn, will cause decreased uptake of amino acids and decreased protein synthesis. The consequences are weakness, muscle wasting & increased susceptibility for infections.
Abstract
Insulin is one of the vital anabolic hormones of the body. It’s naturally produces by the β-cells of the exocrine part of Pancreas. The main function of insulin is regulating glucose metabolism.
High levels of insulin can cause Hyper-insulinemia. Low levels or resistance to insulin can lead to Hyperglycaemia eventually leading to Diabetes.